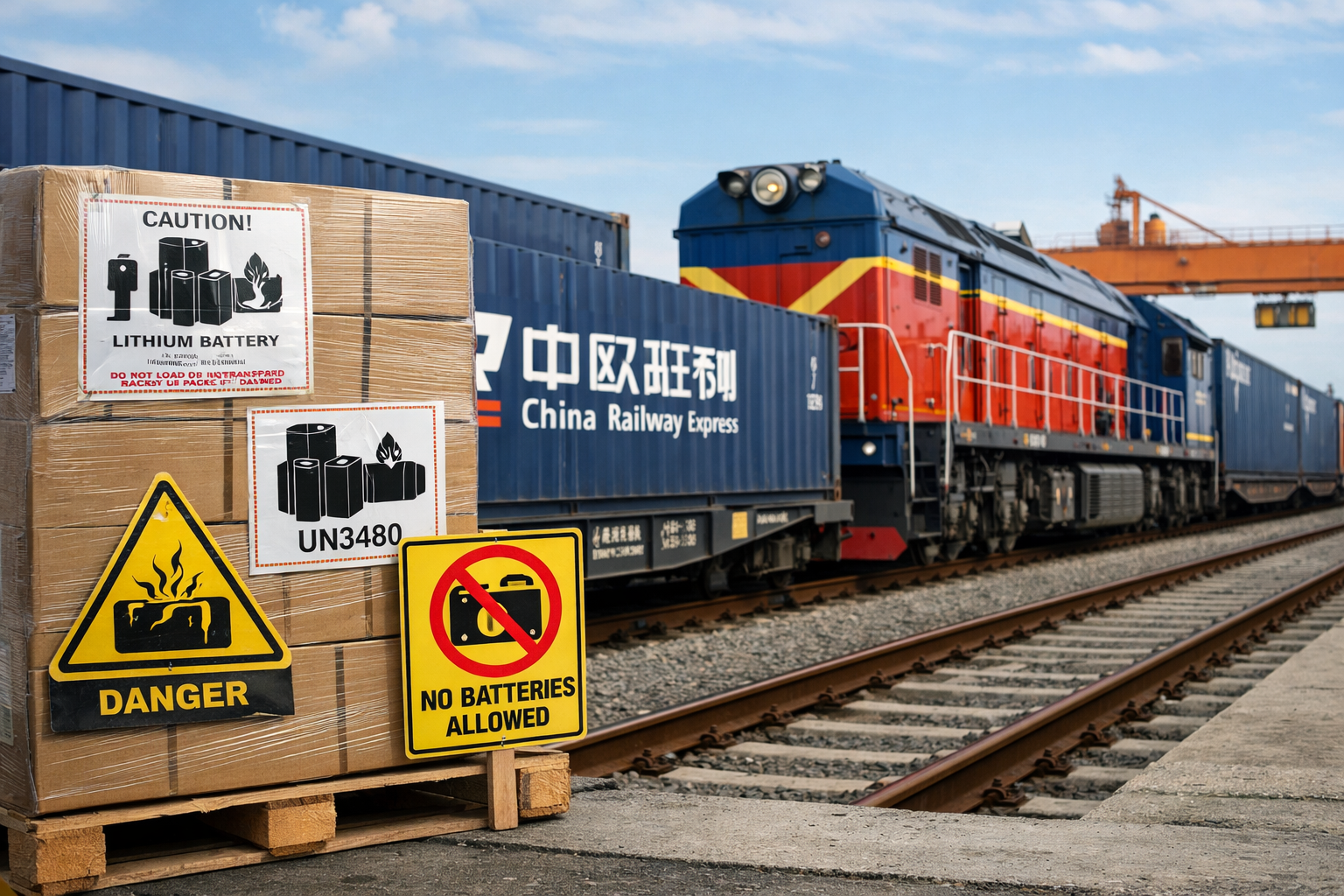

Why Railway Freight Completely Refuses Battery Cargo
Railway freight plays a vital role in Eurasian trade. In recent years, the China Railway Express has connected China with
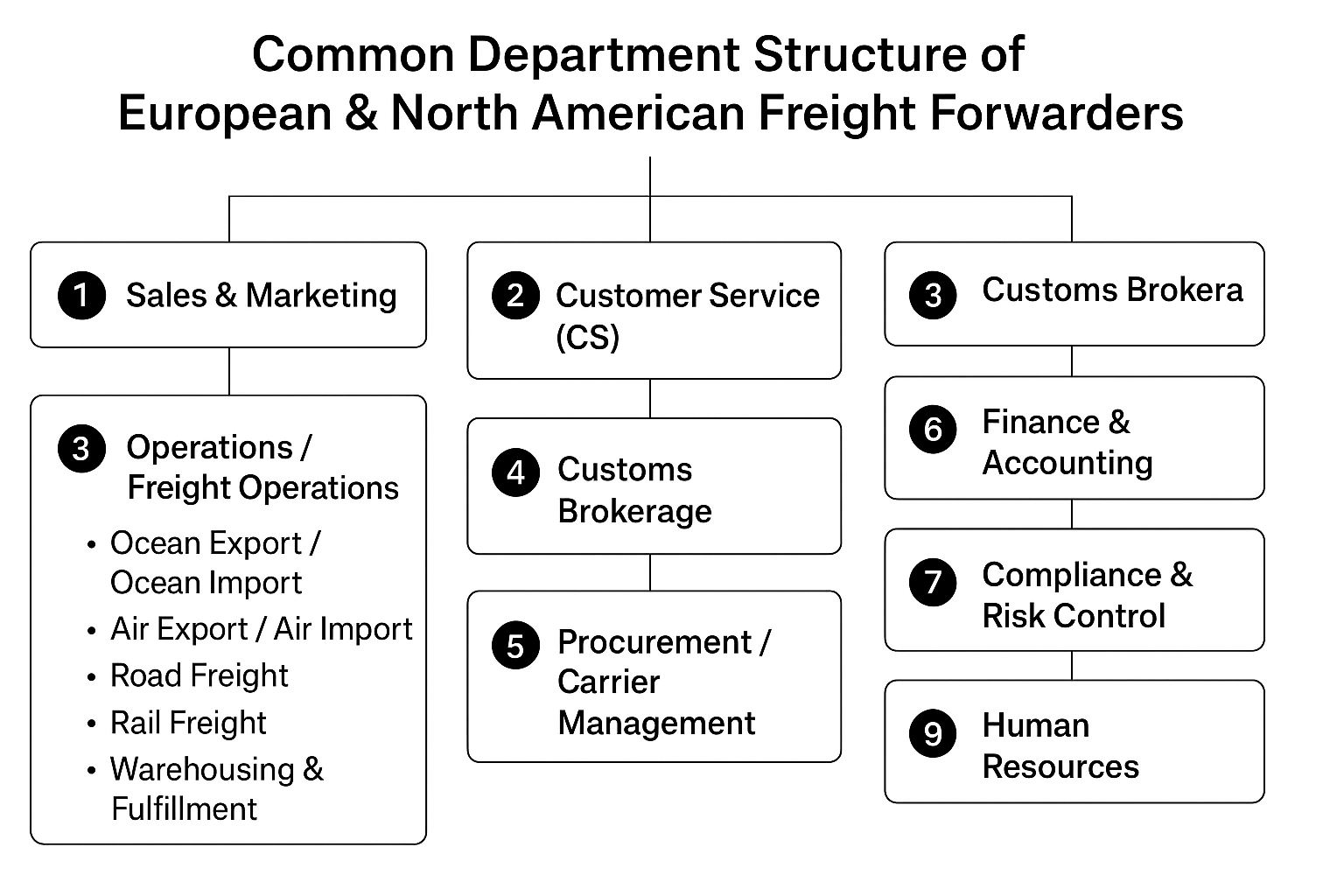
Responsibilities:
Customer acquisition and market development
Brand promotion and digital marketing
Managing key accounts and strategic partnerships
Responsibilities:
Handling booking requests and shipment inquiries
Communicating shipment status and solving exceptions
Coordinating with carriers, warehouses, and operations teams
“Typically divided into Import CS and Export CS.”
Responsibilities:
Booking with carriers, arranging pickup, preparing documents
Managing export/import procedures
Costing, invoicing, and shipment coordination
Common Sub-Teams:
Ocean Export / Ocean Import
Air Export / Air Import
Rail Freight
Warehousing & Fulfillment
Responsibilities:
Import/export customs declaration
HS code classification, duty/tax assessment
Compliance checks and communication with customs authorities
Often handled by Licensed Customs Brokers in the U.S. and Canada.
Responsibilities:
Negotiating rates with ocean, air, and trucking carriers
Managing rate sheets, contracts, and procurement costs
Ensuring service reliability and cost competitiveness
Responsibilities:
Accounts receivable/payable (AR/AP)
Billing, payment, and profit analysis
Managing currency and financial compliance
Responsibilities:
Sanction checks (OFAC/EU Sanctions)
Dangerous goods & restricted cargo oversight
Cargo insurance and claims
Trade compliance documentation
Responsibilities:
TMS system development and maintenance
API/EDI integrations with carriers and customers
Data analytics, automation, and digital tracking tools
Responsibilities:
Recruitment, training, and performance management
Employee relations and HR compliance
Responsibilities:
Strategic planning and multi-department coordination
KPI and performance supervision
Legal review and corporate governance
Freight forwarders play a central role in global trade by acting as logistics integrators, connecting exporters, importers, and carriers across international supply chains. They coordinate transportation by sea, air, road, and rail, handle documentation, customs clearance, and compliance requirements, and optimize routes and costs to ensure goods move efficiently across borders. By leveraging their expertise, carrier networks, and digital platforms, freight forwarders reduce shipping risks, improve transit visibility, and streamline complex international procedures. Their ability to provide end-to-end logistics solutions makes them an essential link in modern global commerce, enabling businesses of all sizes to access overseas markets smoothly and reliably.

Railway freight plays a vital role in Eurasian trade. In recent years, the China Railway Express has connected China with
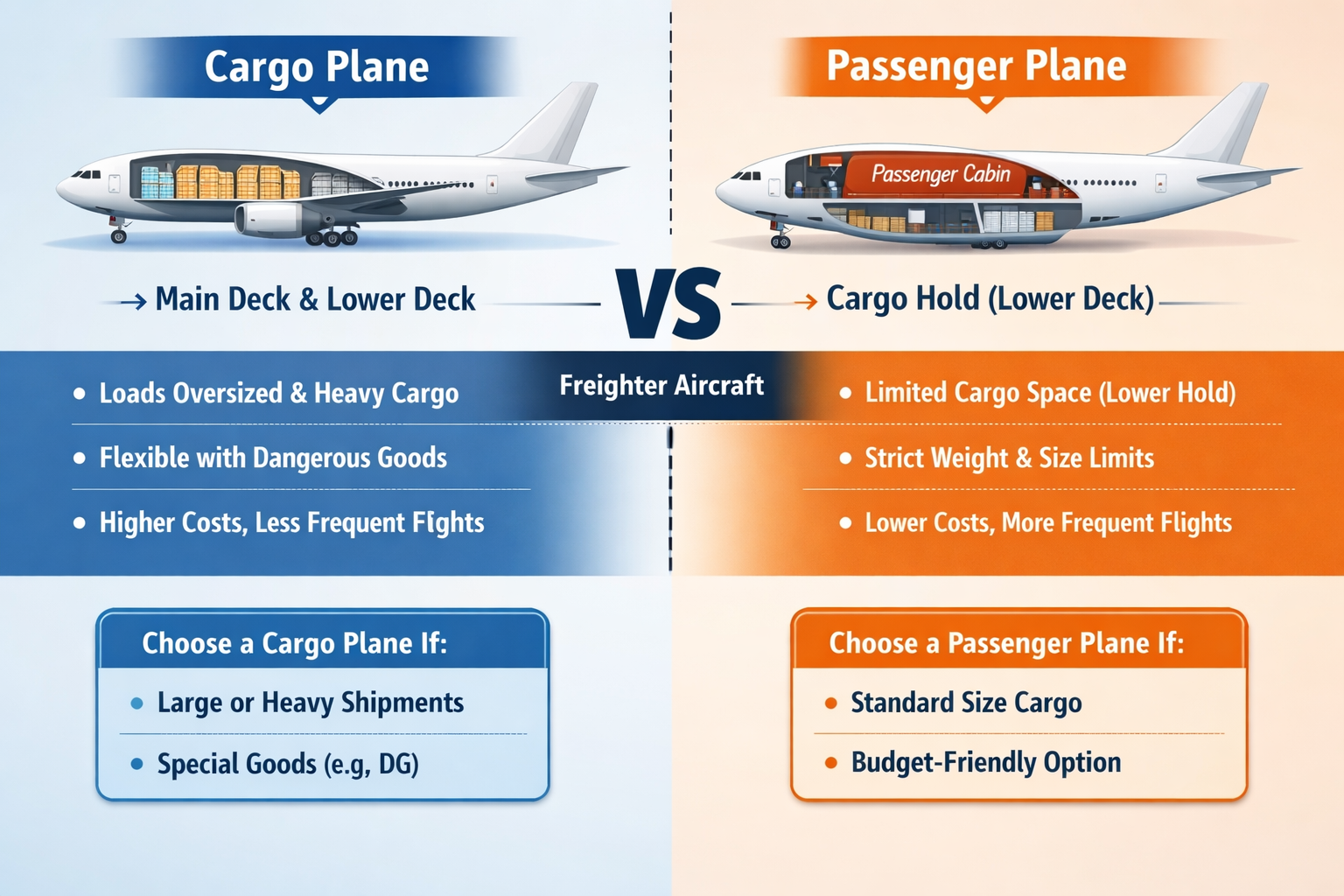
When you ship goods by air, you must first understand which type of aircraft will carry your cargo. Airlines operate